What is Graphic Design? Beginner Guide 2024
Last updated on December 21, 2024 by Digital Sky Star
"The most important thing in business is innovation, and trends and technologies are at its heart."
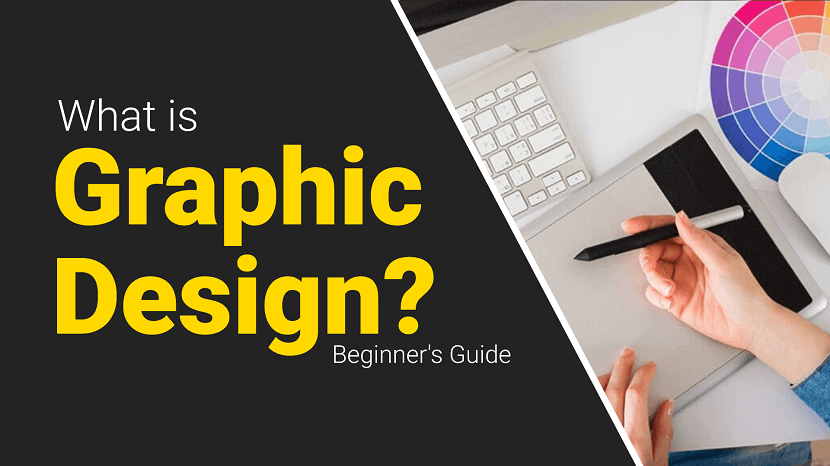
Graphic design is the art and practice of creating visual content to communicate messages. Designers use typography, imagery, color, and layout techniques to craft compelling and effective designs for various media, including print, digital, and environmental graphics. The primary goal is to convey information clearly and engagingly while evoking the desired emotional response from the audience. Graphic design encompasses a wide range of applications, from advertising and branding to web design and product packaging. It requires a blend of creativity and technical skills, often involving software like Adobe Creative Suite. Effective graphic design is essential for businesses and organizations to establish their identity, attract customers, and deliver their messages efficiently. It combines aesthetics and functionality, making it a crucial element in modern visual communication.
Contents Overview
- What is the Main purpose of graphic design?
- What are the Elements of Graphic Design?
- What are the Principles of Graphic Design?
- What are the tools of graphic design?
- What are the Types of Graphic Design?
- Common graphic design jobs
- What does a graphic designer do?
- FAQs
- Conclusion
What is the Main purpose of graphic design?
The main purpose of graphic design is to communicate messages visually in a clear, engaging, and effective manner. It involves the strategic use of typography, imagery, color, and layout to convey information and evoke specific responses from the audience. Graphic design aims to inform, persuade, and captivate viewers, making it a crucial tool for businesses and organizations. It helps establish brand identity, attract and retain customers, and enhance the overall user experience across various media, including print, digital, and environmental graphics. Ultimately, the goal of graphic design is to deliver a message that resonates with the target audience and achieves the desired outcome.
What are the Elements of Graphic Design?
Graphic design relies on several key elements to create visually appealing and effective designs. These elements include:
- Line: Lines are used to create shapes, divide spaces, and guide the viewer's eye. They can be straight, curved, thick, thin, solid, or dashed.
- Shape: Shapes are created by lines and can be geometric (circles, squares, triangles) or organic (freeform, natural shapes). They help to structure the design and can convey different meanings.
- Color: Color influences mood and perception. It is used to attract attention, create harmony, and convey emotions. Color theory involves understanding the relationships between colors and how they interact.
- Texture: Texture refers to the surface quality of an element. It can be visual (simulated) or tactile (physical). Texture adds depth and interest to a design.
- Space: Space refers to the area around and between elements in a design. Positive space is the space occupied by elements, while negative space (or white space) is the empty space around them. Proper use of space creates balance and clarity.
- Form: Form adds depth and dimension to a design. It is often achieved through shading, perspective, and the use of light and shadow to create the illusion of three-dimensionality.
- Typography: Typography is the art of arranging type to make written language legible, readable, and visually appealing. It involves selecting fonts, adjusting spacing, and designing the overall text layout. Check out free fonts to create awesome designs!
- Balance: Balance is the distribution of visual weight in a design. It can be symmetrical (evenly distributed) or asymmetrical (uneven but still balanced). Balance creates stability and structure.
- Contrast: Contrast involves the difference between elements, such as color, shape, size, and texture. High contrast draws attention and emphasizes important elements, while low contrast creates a harmonious and subtle design.
- Hierarchy: Hierarchy is the arrangement of elements to show their order of importance. It guides the viewer's eye through the design, ensuring that the most important information is noticed first.
- Alignment: Alignment refers to the placement of elements in relation to each other. Proper alignment creates a cohesive and organized look, making the design more visually appealing and easier to navigate.
- Repetition: Repetition involves using the same or similar elements throughout the design to create consistency and unity. It helps to reinforce the overall message and makes the design more cohesive.
What are the Principles of Graphic Design?
The principles of graphic design are fundamental guidelines that help designers create visually appealing and effective compositions. These principles include:
- Balance: Balance involves distributing elements evenly within a design to create a sense of stability. It can be symmetrical (equal distribution) or asymmetrical (different but balanced elements).
- Contrast: Contrast is the difference between elements, such as color, size, shape, and texture. It helps to create visual interest, highlight important areas, and distinguish elements from one another.
- Emphasis: Emphasis is about creating a focal point in the design to draw attention to the most important elements. This can be achieved through contrast, color, size, and placement.
- Movement: Movement guides the viewer's eye through the design in a deliberate path. It can be achieved through lines, shapes, and positioning of elements, ensuring that the viewer's attention flows smoothly from one part of the design to another.
- Repetition: Repetition involves using the same or similar elements consistently throughout the design. It creates unity, reinforces concepts, and helps to establish a visual rhythm.
- Proportion: Proportion refers to the relative size and scale of elements within a design. It ensures that elements are appropriately sized in relation to each other, creating a sense of harmony and balance.
- Alignment: Alignment is the arrangement of elements to create a clean, organized, and cohesive look. Proper alignment ensures that elements are visually connected and related to each other.
- Unity: Unity is the harmony between all elements in a design, making them appear as a cohesive whole. It ensures that all parts of the design work together and support the overall message.
- Variety: Variety involves incorporating different elements and styles to create interest and avoid monotony. It can be achieved through contrasting colors, shapes, textures, and sizes.
- Hierarchy: Hierarchy is the organization of elements to show their order of importance. It guides the viewer's eye from the most important information to less critical details, helping to communicate the message effectively.
What are the tools of graphic design?
Graphic designers use a variety of tools to create their work. These tools can be broadly categorized into software, hardware, and traditional tools. Here's a comprehensive list:
Software Tools
1. Adobe Creative Suite:
- Photoshop: For photo editing, image manipulation, and digital painting.
- Illustrator: For vector graphics, illustrations, and logo design.
- InDesign: For layout design, such as magazines, brochures, and books.
2. CorelDRAW: A vector graphics editor used for design and illustration.
3. Sketch: A digital design tool for creating interfaces and user experiences.
4. Figma: A collaborative interface design tool used for prototyping and UI/UX design.
5. Affinity Designer: A vector graphic design software alternative to Adobe Illustrator.
6. Canva: An online platform for creating social media graphics, presentations, posters, and other visual content.
7. Procreate: A digital illustration app for iPad, popular among illustrators and artists.
8. GIMP: An open-source image editor similar to Adobe Photoshop.
Hardware Tools
1. Computer: A powerful desktop or laptop is essential for running graphic design software.
2. Graphics Tablet: Devices like Wacom tablets allow for precise drawing and illustration directly into software.
3. Monitor: High-resolution monitors with accurate color representation are crucial for design work.
4. Scanner: Used to digitize sketches, drawings, or printed materials.
5. Printer: High-quality printers are essential for producing physical copies of designs.
Traditional Tools
1. Sketchbooks and Paper: For brainstorming, sketching ideas, and initial drafts.
2. Pencils and Pens: Essential for drawing, sketching, and inking designs.
3. Markers and Brushes: Used for adding color and texture to sketches and illustrations.
4. Rulers and Compasses: For creating precise lines, shapes, and measurements in traditional design work.
Online Resources and Libraries
1. Stock Photo Websites: Platforms like Shutterstock, Unsplash, and Adobe Stock provide high-quality images for use in designs.
2. Font Libraries: Websites like Google Fonts, Adobe Fonts, and DaFont offer a wide range of typefaces for various design projects.
3. Color Palettes: Tools like Adobe Color help designers choose and create harmonious color schemes.
What are the Types of Graphic Design?
Graphic design encompasses a wide range of specializations, each serving different purposes and industries. Here are some of the main types of graphic design:
- Visual Identity Graphic Design: This type involves creating brand elements such as logos, color schemes, typography, and brand guidelines to establish a cohesive visual identity for a company or organization.
- Marketing & Advertising Graphic Design: Designers in this field create visuals for promotional materials like flyers, brochures, posters, banners, social media ads, and email campaigns to attract and engage customers.
- User Interface (UI) Graphic Design: UI designers focus on the visual aspects of user interfaces for websites, apps, and software, ensuring an attractive and intuitive user experience.
- Publication Graphic Design: This includes designing layouts and covers for printed and digital publications such as books, magazines, newspapers, and e-books, focusing on typography, imagery, and overall layout.
- Packaging Graphic Design: Designers in this area create the visual aspects of product packaging, including the shape, graphics, colors, and typography, to protect the product and attract customers.
- Motion Graphic Design: This involves creating animated graphics for videos, television, websites, and other multimedia platforms. It includes elements like animation, visual effects, and cinematic techniques.
- Environmental Graphic Design: This type merges graphic design, architecture, and interior design to create visually engaging environments. Examples include signage, wayfinding systems, exhibition designs, and themed environments.
- Art and Illustration for Graphic Design: This specialization involves creating original artwork for various contexts, such as posters, t-shirts, album covers, book illustrations, and digital art.
- Web Design: Web designers create the layout, visual design, and interactive elements of websites, focusing on aesthetics, usability, and the overall user experience.
- Information Graphic Design (Infographics): Designers create visual representations of data and information, making complex data more accessible and easier to understand through charts, diagrams, and maps.
- Typography: Typography designers specialize in creating and arranging type to make text readable, appealing, and effective in communication. They work on designing typefaces, fonts, and other text-based elements.
- Corporate Design: This involves designing corporate identity materials like business cards, letterheads, envelopes, and other stationery that represent a company's brand.
Common graphic design jobs
Graphic design offers a variety of career opportunities across different industries. Here are some common graphic design jobs:
- Graphic Designer: Creates visual content for various media, including print, digital, and social media. They work on projects such as logos, brochures, advertisements, and websites.
- Art Director: Oversees the visual style and creative direction of projects. They manage design teams and ensure that the overall visual presentation aligns with the client's or organization's goals.
- Creative Director: Responsible for the overall creative vision of a project or campaign. They lead the creative team, make high-level creative decisions, and coordinate with clients or stakeholders.
- UI/UX Designer: Focuses on designing user interfaces (UI) and user experiences (UX) for websites, apps, and software. They ensure that products are visually appealing, intuitive, and user-friendly.
- Web Designer: Specializes in creating the visual design and layout of websites. They work on elements like graphics, color schemes, typography, and overall site structure to ensure an engaging user experience.
- Motion Graphic Designer: Creates animated graphics and visual effects for videos, films, television, and online media. They use animation software to bring static designs to life.
- Brand Identity Designer: Develops visual elements that represent a brand's identity, including logos, color palettes, typography, and brand guidelines. They ensure consistency across all brand materials.
- Illustrator: Produces original artwork for various applications, such as books, magazines, advertisements, and digital media. They create detailed illustrations and visual concepts.
- Packaging Designer: Designs the visual and structural aspects of product packaging. They create packaging that is both functional and visually appealing to attract customers and protect the product.
- Publication Designer: Works on the layout and design of printed and digital publications, such as books, magazines, newspapers, and e-books. They focus on typography, imagery, and overall page design.
- Environmental Graphic Designer: Merges graphic design with architecture and interior design to create visually engaging environments. This includes designing signage, wayfinding systems, and exhibition displays.
- Infographic Designer: Specializes in creating visual representations of data and information. They design charts, diagrams, and maps to make complex information more accessible and understandable.
- Freelance Graphic Designer: Works independently, offering design services to various clients on a project-by-project basis. They may work in multiple areas of graphic design depending on their skills and client needs.
- Marketing Designer: Creates visual content for marketing campaigns, including social media graphics, email templates, advertisements, and promotional materials. They work closely with marketing teams to ensure consistent messaging.
- Visual Designer: Focuses on the overall aesthetics of a project, working on both web and print designs. They ensure that the visual elements align with the brand's identity and communication goals.
What does a graphic designer do?
A graphic designer uses visual elements to create designs that communicate messages effectively and aesthetically. Their responsibilities can vary widely depending on the specific job and industry but generally include the following tasks:
- Understanding Project Requirements: Collaborating with clients, marketing teams, or other stakeholders to understand the project's goals, target audience, and specific requirements.
- Concept Development: Brainstorming and developing creative concepts that align with the project’s objectives. This often involves sketching ideas, creating mood boards, and exploring different design approaches.
- Creating Visual Content: Using design software to create graphics, layouts, and illustrations. This can include logos, brochures, advertisements, websites, social media graphics, packaging, and more.
- Selecting Colors, Fonts, and Images: Choosing appropriate color schemes, typography, and imagery that enhance the overall design and ensure brand consistency.
- Layout and Composition: Arranging text, images, and other design elements in a way that is visually appealing and easy to read. This involves understanding principles of balance, contrast, alignment, and hierarchy.
- Prototyping and Mockups: Creating prototypes or mockups of designs to present to clients or stakeholders for feedback. This can include digital mockups for websites and apps or physical mockups for print materials.
- Revising and Refining Designs: Making revisions based on feedback from clients or stakeholders. This iterative process ensures that the final design meets all requirements and expectations.
- Preparing Final Files: Ensuring that all design files are properly formatted and ready for production, whether for print or digital use. This includes exporting files in the correct resolution and format.
- Collaborating with Other Professionals: Working with other creative professionals such as photographers, illustrators, web developers, and printers to bring the design to life.
- Keeping Up with Design Trends: Staying informed about current design trends, tools, and technologies to ensure that their work remains fresh and relevant.
- Project Management: Managing multiple projects simultaneously, meeting deadlines, and ensuring that all aspects of the project stay on track.
FAQs
1. What is graphic design?
Answer : Graphic design is the art and practice of creating visual content to communicate messages. It involves the use of typography, imagery, color, and layout techniques to produce designs for various media, including print, digital, and environmental graphics.
2. What does a graphic designer do?
Answer : A graphic designer creates visual content to communicate messages effectively and aesthetically. They work on projects such as logos, brochures, websites, advertisements, and packaging. Their tasks include concept development, creating designs using software, selecting colors and fonts, and collaborating with clients and other professionals.
3. What software do graphic designers use?
Answer : Graphic designers commonly use software like Adobe Photoshop, Illustrator, and InDesign. Other popular tools include CorelDRAW, Sketch, Figma, Affinity Designer, Canva, and Procreate.
4. What are the key elements of graphic design?
Answer : The key elements of graphic design include line, shape, color, texture, space, form, typography, balance, contrast, hierarchy, alignment, and repetition. These elements work together to create visually appealing and effective designs.
5. What are the principles of graphic design?
Answer : The principles of graphic design include balance, contrast, emphasis, movement, repetition, proportion, alignment, unity, variety, and hierarchy. These principles guide the organization and arrangement of design elements to achieve a cohesive and effective visual composition.
6. How do I become a graphic designer?
Answer : To become a graphic designer, you typically need a combination of education and practical experience. Many graphic designers have a degree in graphic design or a related field. Building a strong portfolio, learning design software, and gaining experience through internships or freelance work are also important steps.
7. What is the difference between UI and UX design?
Answer : UI (User Interface) design focuses on the visual aspects of a product, such as layout, colors, and typography. UX (User Experience) design, on the other hand, is concerned with the overall feel of the product, including usability, accessibility, and the user's interaction with the product. Both UI and UX designers work together to create seamless and enjoyable user experiences.
8. What is a brand identity?
Answer : Brand identity is the collection of visual elements that represent a brand, including its logo, color palette, typography, imagery, and overall style. It helps to create a cohesive and recognizable image for the brand, distinguishing it from competitors.
9. How important is color in graphic design?
Answer : Color is a critical element in graphic design as it influences mood, perception, and brand recognition. It can attract attention, convey emotions, and create visual harmony. Understanding color theory and how colors interact is essential for effective design.
10. What is the role of typography in graphic design?
Answer : Typography involves the selection and arrangement of type to make written language legible, readable, and visually appealing. It plays a crucial role in establishing hierarchy, setting the tone, and enhancing the overall aesthetic of a design.
11. What are some common graphic design jobs?
Answer : Common graphic design jobs include graphic designer, art director, creative director, UI/UX designer, web designer, motion graphic designer, brand identity designer, illustrator, packaging designer, publication designer, environmental graphic designer, and marketing designer.
12. What is the difference between raster and vector graphics?
Answer : Raster graphics are made up of pixels and are resolution-dependent, meaning they can lose quality when scaled. Examples include photographs and digital paintings. Vector graphics, on the other hand, are created using mathematical equations and can be scaled indefinitely without losing quality. Examples include logos and illustrations created in Adobe Illustrator.
Conclusion
Graphic design is a dynamic and multifaceted field that plays a crucial role in today's visual communication landscape. By combining artistic creativity with technical skills, graphic designers create compelling visual content that informs, persuades, and captivates audiences across various media. Understanding the elements and principles of design, mastering essential tools, and staying updated with industry trends are vital for success in this profession.
Graphic design encompasses diverse specializations, including branding, marketing, web design, and environmental graphics, each requiring a unique blend of creativity and technical expertise. Whether crafting a logo that defines a brand's identity or designing a user interface that enhances digital experiences, graphic designers shape the way we perceive and interact with the world around us.
In an increasingly visual culture, the demand for skilled graphic designers continues to grow. Aspiring designers must cultivate their skills, build a strong portfolio, and stay adaptable to the ever-evolving design landscape. Ultimately, graphic design is about solving problems through visual communication, making it an indispensable discipline in our modern, visually-driven society.
"Technology is best when it brings people together." – Matt Mullenweg
If you would like more information about the What is Graphic Design? Beginner Guide 2024, please send us an email.
Written by Digital Sky Star
Trends and Technologies
Trends and Technologies are shaping the future with innovations in AI, IoT, blockchain, and more. Stay updated on the latest advancements transforming industries worldwide. Explore cutting-edge tools, insights, and breakthroughs that drive progress and efficiency. Unlock potential, embrace change, and stay ahead in the ever-evolving tech landscape.
